
Luis Miguel Villada of the UBB and CMM associate researcher heads the initiative in which scientists from Colombia and France also contribute.
As reported in the last days of February, eight international partnership projects were selected this year by the MATH-AmSud competition, a regional scientific-technological cooperation program in which researchers and institutions from Argentina, Brazil, Chile, Colombia, Ecuador, Paraguay, Peru, Uruguay, Venezuela and France participate, to promote and strengthen collaboration and the creation of research and development networks in the field of Mathematics, through the implementation of joint projects.

Dr. Luis Miguel Villada
One of the initiatives that will access this funding is entitled NOTION: NOn-local conservaTION laws for engineering, biological and epidemiological applications, directed by Dr. Luis Miguel Villada Osorio, academic at the Universidad del Bío-Bío (UBB), and researcher at the Centro de Investigación en Ingeniería Matemática (CI²MA), of the Universidad de Concepción (UdeC).
The research team is completed by Paola Goatin (INRIA-Sophia-Antipolis-Mediterrane, France), Christophe Chalons (University of Versailles, France), Abraham Arenas (University of Cordoba, Colombia), and Raimund Bürger, UdeC academic and Deputy Director of CI²MA. “This new challenge is the natural continuation of the previous collaboration with researchers Goatin, Bürger and Chalons, in particular the Inria Associate Team NOLOCO project (2018-2020) aimed at the study of high-order numerical schemes for Conservation Law Systems with emphasis on sedimentation and vehicular traffic models and which, in addition, now aims to address new topics in numerical analysis for epidemiology problems in collaboration with Professor Arenas,” explained Villada, also a researcher at the Center for Mathematical Modeling (CMM) of the University of Chile.
“This type of initiative is at the very core of our work as a research center. It is very important for us to have contact with researchers from all over the world in order to make our advances known and to learn from scientific experiences in other parts of the world. Drs. Villada and Bürger receive our most sincere congratulations and best wishes for success in the development of this project,” said Dr. Rodolfo Araya Durán, Director of CI²MA.
“This project aims to address the analytical and numerical challenges mentioned above, focusing on engineering applications (sedimentation, traffic, population dynamics, etc.) and biological and epidemiological phenomena, and will also allow research stays for the researchers and thesis students involved,” said Villada.
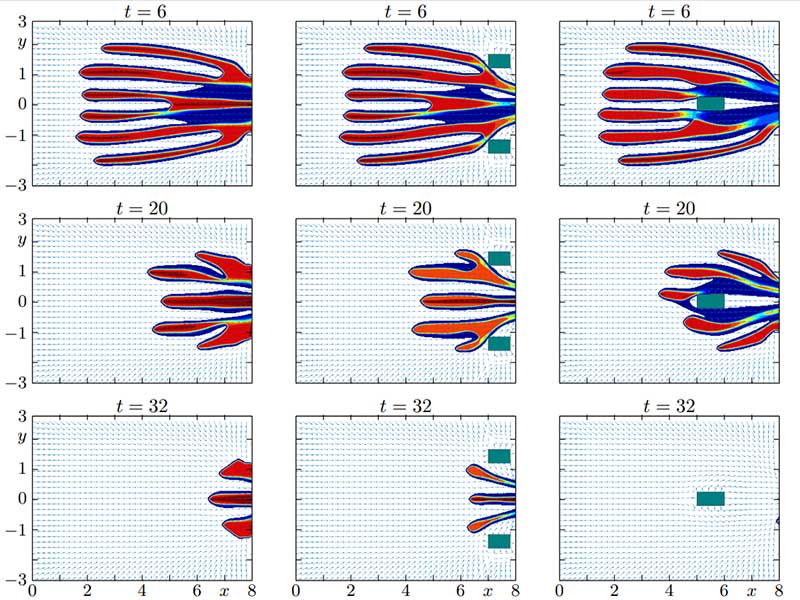 Pattern formation in a population evacuation problem in three different scenarios.
Pattern formation in a population evacuation problem in three different scenarios.
“The conservation laws with non-local flow function”, the scientist deepened, “which depend on integral evaluations of the conserved quantities, arise in several models that describe engineering, biological and epidemiological applications” and, in this sense, explained the Dr. in Applied Sciences with mention in Mathematical Engineering of the UdeC, “the new challenges of this project”, he continued, “are concentrated in developing, analyzing and implementing new mathematical models based on systems of non-linear and non-local partial differential equations”.
These models have applications in diverse problems: vehicular traffic, as a study of models in networks, multi-lane, double lanes and those where speed is discontinuous; pedestrian dynamics, as a study of models that allow the identification of movement patterns and the design of high order WENO type schemes, which preserve positivity or the maximum principle; and in epidemiology, in the design and analysis of models that represent the transmission dynamics of the COVID-19 virus, applying control techniques to identify parameters with a higher incidence of the disease.
On the other hand, Villada stated, “the presence of non-local terms means that the classical techniques developed for hyperbolic systems of conservation laws cannot be applied, which requires the development of new analytical and numerical tools. In addition, the presence of integral terms has a great impact on the cost of numerical simulations, which motivates the design of efficient approximation schemes”.
By Iván R. Tobar
Posted on Mar 22, 2022 in News




 Noticias en español
Noticias en español
